Pediatric sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that affects children of all ages. It occurs when a child experiences repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and various health issues. Understanding this condition is essential for parents and caregivers to ensure proper diagnosis and management.
What is Pediatric Sleep Apnea?
Pediatric sleep apnea is characterized by partial or complete obstruction of the airway during sleep, leading to reduced airflow and oxygen levels. The two main types are:
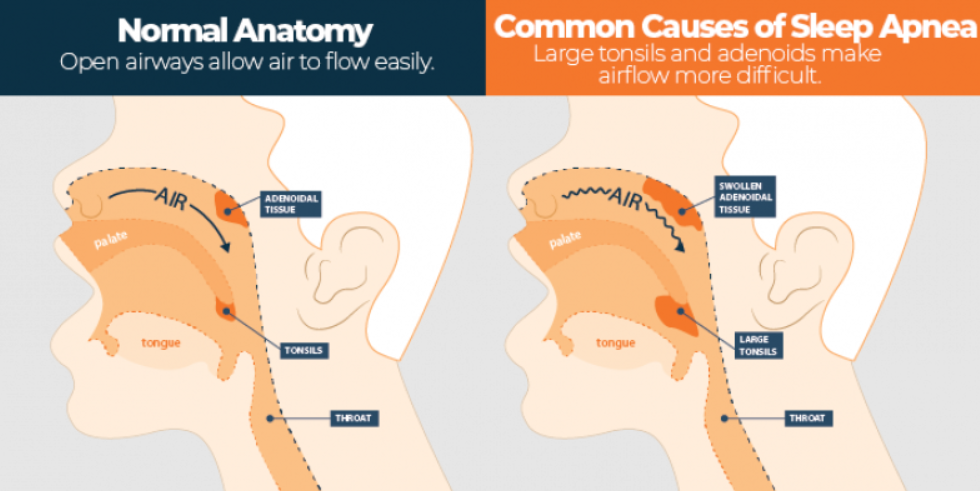
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common form, resulting from a blockage in the upper airway, often due to enlarged tonsils or adenoids.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): This is less common in children and occurs when the brain fails to send appropriate signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Causes of Pediatric Sleep Apnea
Several factors can contribute to sleep apnea in children, including:
- Enlarged Tonsils and Adenoids: The most frequent cause of obstructive sleep apnea in children is the enlargement of these lymphoid tissues, which can obstruct the airway during sleep.
- Obesity: Increased weight can lead to excess fatty tissue in the neck, contributing to airway obstruction.
- Neuromuscular Disorders: Conditions affecting muscle control may result in impaired breathing patterns during sleep.
Anatomical Abnormalities: Certain physical traits, such as a small jaw or a large tongue, can predispose a child to sleep apnea.
Symptoms of Pediatric Sleep Apnea
Identifying sleep apnea in children can be challenging, as symptoms may vary. Common signs include:
- Loud Snoring: Persistent and loud snoring is often the first indicator.
- Pauses in Breathing: Observed by parents, these pauses can last for several seconds and may be followed by gasping or choking sounds.
- Restless Sleep: Frequent tossing and turning during sleep can disrupt the child’s rest.
- Daytime Sleepiness: Children may struggle to stay awake during the day, experiencing fatigue or irritability.
- Behavioral Issues: Increased hyperactivity, difficulty concentrating, or mood swings can be related to poor sleep quality.
Complications of Untreated Sleep Apnea
If left untreated, pediatric sleep apnea can lead to several complications, including:
- Cognitive Impairment: Disrupted sleep can affect memory, learning, and overall cognitive function.
- Behavioral Problems: Sleep deprivation can result in behavioral issues similar to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Growth Delays: Poor sleep quality may impact growth hormone release, leading to growth delays in children.
Cardiovascular Issues: Chronic oxygen deprivation can put strain on the heart and increase the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular problems.
Diagnosis of Pediatric Sleep Apnea
Diagnosing pediatric sleep apnea typically involves a thorough evaluation, including:
- Medical History: A detailed history of sleep patterns, behaviors, and any associated symptoms.
- Physical Examination: An examination of the throat, nose, and mouth to assess for anatomical abnormalities.
- Sleep Studies: Polysomnography (a sleep study) may be conducted to monitor breathing, oxygen levels, and sleep patterns during the night.
Treatment Options for Pediatric Sleep Apnea
Treatment for pediatric sleep apnea depends on the severity of the condition and its underlying causes. Options may include:
- Lifestyle Modifications
Encouraging healthy habits, such as maintaining a healthy weight, promoting regular sleep schedules, and avoiding allergens can help manage mild cases.
- Medical Management
In some instances, medications may be prescribed to address underlying conditions, such as allergies or inflammation.
- Surgical Interventions
If enlarged tonsils or adenoids are identified as the primary cause, surgical removal (adenotonsillectomy) may be recommended. This procedure can significantly improve airway function and alleviate symptoms.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
In cases where surgery is not an option or in more severe instances of sleep apnea, CPAP therapy may be used to keep the airway open during sleep by delivering a continuous flow of air through a mask.
Conclusion
Pediatric sleep apnea is a significant health concern that can impact a child’s quality of life and development. Early recognition and intervention are crucial to preventing complications. If you suspect that your child may be experiencing symptoms of sleep apnea, it is essential to seek professional evaluation and treatment. At Medikeri Hospital, our experienced team is dedicated to providing comprehensive care for children with sleep apnea, ensuring they receive the appropriate diagnosis and management for a healthier future.